 Many people can identify with lice infection but not many people know that pubic lice infection is a sexually transmitted disease and is a marker of other sexually transmitted diseases. In children, it may also be a marker of sexual abuse and is something that must be investigated further.
Many people can identify with lice infection but not many people know that pubic lice infection is a sexually transmitted disease and is a marker of other sexually transmitted diseases. In children, it may also be a marker of sexual abuse and is something that must be investigated further.
Head lice are common in school children especially amongst ages 3-12 years with the highest incidence during summer. It is not a reason to keep kids out of school. Children should return to school after treatment but may need repeat treatment in about a week.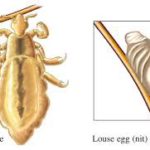
People with lice infection may have itchiness of the scalp which may increase at night when the lice feed but it may be asymptomatic too especially in children
Many believe incorrectly that lice infection is associated with low socioeconomic status, a frequency of shampooing/brushing, poor hygiene or long hair.
About the louse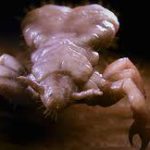
The head louse is about 1-2 mm long and wingless. It has a white/gray color and lives on average for about 30 days.It Inserts its mouth into the skin and feeds on blood of its human host every 4-6 hours. It reproduces by laying eggs at night at hair follicle base of head hair, pubic hair or seams of clothing (body lice)
Prevention
Clean all clothing and stuffed animals (minimum water temperature of 50°C) 
Clean and vacuum the house, it is not necessary to fumigate the house
Avoid sharing combs, brushes, headgear, caps or hats and soak hair grooming items in hot water.
Avoid head-to-head contact
Avoid storing other people’s clothing together
 Treatment
Treatment
Permethrin 1% cream rinse (may repeat in 7-10 days)
Permethrin 5% may be more effective in some cases.